Hi Dear Learners!
Welcome to Android Learning.What is Android?
 Android is a software package and linux based operating system for mobile devices such as tablet computers and smartphones.
Android is a software package and linux based operating system for mobile devices such as tablet computers and smartphones.It is developed by Google and later the OHA (Open Handset Alliance). Java language is mainly used to write the android code even though other languages can be used.
The goal of android project is to create a successful real-world product that improves the mobile experience for end users.
What is Open Handset Alliance (OHA) ?
 It's a consortium of 84 companies such as google, samsung, AKM, synaptics, KDDI, Garmin, Teleca, Ebay, Intel etc.
It's a consortium of 84 companies such as google, samsung, AKM, synaptics, KDDI, Garmin, Teleca, Ebay, Intel etc.It was established on 5th November, 2007, led by Google. It is committed to advance open standards, provide services and deploy handsets using the Android Plateform.
Features of Android
There are many advantages of android. They are as follows:* It is open-source.
* Anyone can customize the Android Platform.
* There are a lot of mobile applications that can be chosen by the consumer.
* It provides many interesting features like weather details, opening screen, live RSS (Really Simple Syndication) feeds etc.
* It provides support for messaging services(SMS and MMS), web browser, storage (SQLite), connectivity (GSM, CDMA, Blue Tooth, Wi-Fi etc.), media, handset layout etc.
Categories of Android applications
 There are many android applications in the market. The top categories are:
There are many android applications in the market. The top categories are:- Entertainment
- Tools
- Communication
- Productivity
- Personalization
- Music and Audio
- Social
- Media and Video
- Travel and Local etc.
History of Android
The history and versions of android are interesting to know. The code names of android ranges from A to J currently, such as Aestro, Blender, Cupcake, Donut, Eclair, Froyo, Gingerbread, Honeycomb, Ice Cream Sandwitch,Jelly Bean and KitKat. Let's understand the android history pointy:- Initially, Andy Rubin founded Android Incorporation in Palo Alto, California, United States in October, 2003.
- In 17th August 2005, Google acquired android Incorporation. Since then, it is in the subsidiary of Google Incorporation.
- The key employees of Android Incorporation are Andy Rubin, Rich Miner, Chris White and Nick Sears.
- Originally intended for camera but shifted to smart phones later because of low market for camera only.
- Android is the nick name of Andy Rubin given by coworkers because of his love to robots.
- In 2007, Google announces the development of android OS.
- In 2008, HTC launched the first android mobile.
Android Versions, Codename and API
Let's see the android versions codename and API provided by Google.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Android Software StackAndroid software stack (also known as android architecture) includes linux kernel, native libraries (middleware), Android Runtime, Application Framework and Applications.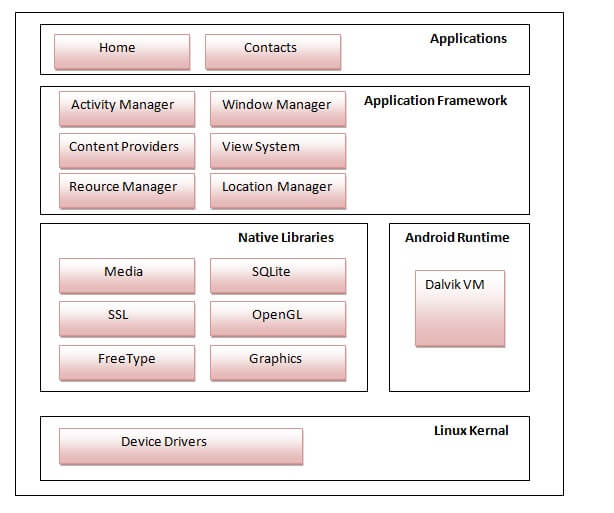 Linux kernel is responsible for device drivers, power management, resource access etc. OS tasks.
Linux kernel is responsible for device drivers, power management, resource access etc. OS tasks.On the top of linux kernel, their are Native libraries such as WebKit, OpenGL, FreeType, SQLite, Media, C runtime library (libc) etc. The WebKit library is responsible for browser support, SQLite is for database, FreeType for font support, Media for playing and recording audio and video formats. The main Android API's are UI (User Interface), telephony, resources, locations, Content Providers (data) and package managers. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Android Core Building Blocks A component is simply a piece of code that has a well defined life cycle e.g. Activity, Receiver, Service etc.
A component is simply a piece of code that has a well defined life cycle e.g. Activity, Receiver, Service etc. The core building blocks or fundamental components of android are activities, views, intents, services, content providers, fragments and AndroidManifest.xml. ActivityAn activity is a class that represents a single screen. It is like a Frame in AWT.ViewA view is the UI element such as button, label, text field etc. Anything that you see is a view.IntentIntent is used to invoke components. It is mainly used to:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ServiceService is a background process that can run for a long time.There are two types of services local and remote. Local service is accessed from within the application whereas remote service is accessed remotely from other applications running on the same device. Content ProviderContent Providers are used to share data between the applications.FragmentFragments are like parts of activity. An activity can display one or more fragments on the screen at the same time.AndroidManifest.xmlIt contains informations about activities, content providers, permissions etc. It is like the web.xml file in Java EE.Android Virtual Device (AVD)It is used to test the android application without the need for mobile or tablet etc. It can be created in different configurations to emulate different types of real devices. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Android EmulatorAndroid Emulator is used to run, debug and test the android application. If you don't have the real device, it can be the best way to run, debug and test the application.It uses an open source processor emulator technology called QEMU. The emulator tool enables you to start the emulator from the command line. You need to write: emulator -avd In the given image, you can see the android emulator, it displays the output of the hello android example. 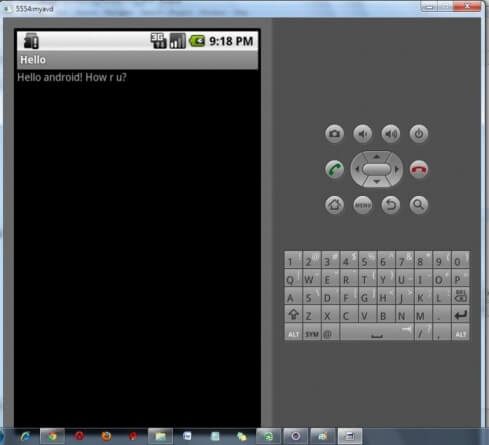 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
What is an Inflater? and how it is used?
Layout inflation is the term used within the context of Android to indicate when an XML layout resource is parsed and converted into a hierarchy of View objects.
When you use a custom view in a
public MyAdapter(Context context, List<MyObject> objects) extends ArrayAdapter {
super(context, 1, objects);
/* We get the inflator in the constructor */
mInflater = (LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
View view;
/* We inflate the xml which gives us a view */
view = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.my_list_custom_row, parent, false);
/* Get the item in the adapter */
MyObject myObject = getItem(position);
/* Get the widget with id name which is defined in the xml of the row */
TextView name = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.name);
/* Populate the row's xml with info from the item */
name.setText(myObject.getName());
/* Return the generated view */
return view;
}
ListView you must define the row layout. You create an xml where you place android widgets and then in the adapter's code you have to do something like this:public MyAdapter(Context context, List<MyObject> objects) extends ArrayAdapter {
super(context, 1, objects);
/* We get the inflator in the constructor */
mInflater = (LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
View view;
/* We inflate the xml which gives us a view */
view = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.my_list_custom_row, parent, false);
/* Get the item in the adapter */
MyObject myObject = getItem(position);
/* Get the widget with id name which is defined in the xml of the row */
TextView name = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.name);
/* Populate the row's xml with info from the item */
name.setText(myObject.getName());
/* Return the generated view */
return view;
}
Note: This Blog is under Construction!


